Universal immunization programs stand as a beacon of hope in the fight against preventable diseases, offering a lifeline to individuals and communities worldwide. This global initiative, rooted in the principle of equitable access to life-saving vaccines, has revolutionized public health, dramatically reducing disease burden and saving countless lives.
From its humble beginnings, the concept of universal immunization has evolved into a sophisticated and comprehensive approach to disease prevention. This journey, marked by scientific breakthroughs and unwavering commitment, has resulted in the eradication of smallpox and the near-elimination of polio, serving as testaments to the power of vaccination.
Introduction to Universal Immunization Programs
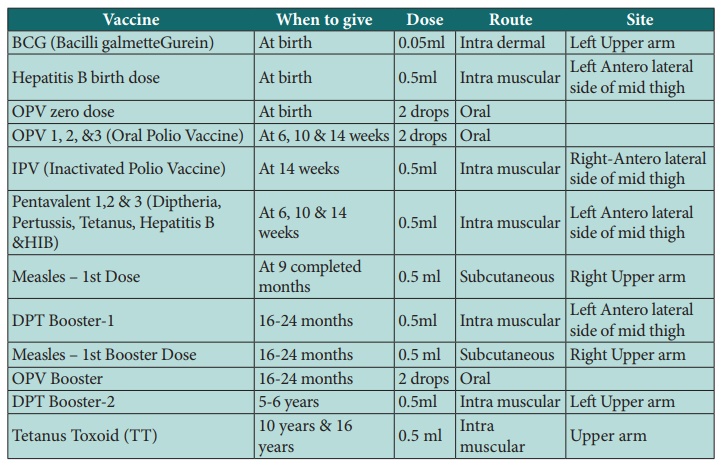
Universal immunization programs aim to provide routine vaccinations to all individuals within a population, regardless of their socioeconomic status, geographic location, or other factors. These programs play a crucial role in preventing vaccine-preventable diseases and improving public health.
The concept of universal immunization emerged in the early 20th century, with the development of vaccines against diseases such as smallpox, diphtheria, and tetanus. The World Health Organization (WHO) played a pivotal role in promoting and supporting universal immunization programs globally.
Rationale and Objectives of Universal Immunization Programs
Universal immunization programs are based on the principle of herd immunity, which occurs when a significant proportion of the population is immune to a disease, making it difficult for the disease to spread. This protects not only those who are vaccinated but also those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons.
The primary objectives of universal immunization programs are:
- To reduce the incidence and mortality rates of vaccine-preventable diseases.
- To protect vulnerable populations, such as infants, young children, and the elderly, from infectious diseases.
- To contribute to the overall improvement of public health and well-being.
- To achieve equitable access to immunization services for all individuals, regardless of their background.
Benefits of Universal Immunization Programs

Universal immunization programs are a cornerstone of public health, offering a wide range of benefits that extend beyond individual health to encompass communities and societies as a whole. These programs play a crucial role in protecting individuals from preventable diseases, reducing the burden on healthcare systems, and fostering economic growth.
Impact on Individual Health
Universal immunization programs significantly impact individual health by protecting people from potentially deadly and debilitating diseases. Vaccinations work by exposing the body to a weakened or inactive form of a virus or bacteria, enabling the immune system to develop antibodies that fight off the disease if exposed in the future. This protection extends beyond the individual, contributing to herd immunity, where a high percentage of the population is immune, making it difficult for diseases to spread.
Benefits for Communities and Societies, Universal immunization program
Universal immunization programs have profound benefits for communities and societies, promoting overall health and well-being.
- Reduced Disease Burden: Immunization programs significantly reduce the incidence of preventable diseases, leading to fewer hospitalizations, disabilities, and deaths. This alleviates the burden on healthcare systems, freeing up resources for other health priorities.
- Improved Child Survival: Immunization programs are particularly crucial for children, who are highly susceptible to vaccine-preventable diseases. By protecting children, these programs contribute to increased life expectancy and improve the overall health of future generations.
- Enhanced Economic Productivity: By preventing illness and disability, universal immunization programs contribute to a healthier and more productive workforce. This translates into increased economic output and a more robust economy.
Economic Benefits
Universal immunization programs deliver substantial economic benefits, both directly and indirectly.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The cost of vaccinating a population is far outweighed by the savings generated from preventing diseases and their associated costs, such as healthcare expenses, lost productivity, and disability payments. Studies have shown that immunization programs have a high return on investment, making them a cost-effective public health intervention.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Immunization programs reduce the incidence of preventable diseases, leading to fewer hospitalizations, outpatient visits, and medication costs. This translates into significant savings for individuals, families, and healthcare systems.
- Economic Growth: By promoting a healthy and productive workforce, universal immunization programs contribute to economic growth and development. A healthier population is more likely to participate in the workforce, contributing to increased productivity and economic output.
Last Point
The future of universal immunization holds immense promise, with advancements in vaccine technology paving the way for more effective, targeted, and accessible interventions. As we strive for a world free from preventable diseases, the collective efforts of governments, healthcare professionals, and communities remain crucial in ensuring that every individual has the opportunity to benefit from the life-saving power of vaccines.
Universal immunization programs are essential for protecting communities from preventable diseases. Just as these programs aim to ensure widespread protection, GE universal remote programming allows for the control of multiple devices with a single remote. Both initiatives work to simplify complex systems and provide greater control and convenience, ultimately contributing to a healthier and more efficient world.
